SimpleJdbcCall
Steps to develop spring JDBC application by using SimpleJdbcCall
1) create new maven project.
2) add required dependencies in POM.xml file
Spring JDBC dependency, oracle/sql driver etc.!
3) create beans configured Java/xml file.
4) write business logic inside src/main/java
5) create procedure/ function for calling data from database
Spring JDBC provides multiple templates to interact with Databases i.e., JdbcTemplate, NamedParameterJdbcTemplate,SimpleJdbcInsert, SimpleJdbcCall
based on requirement we can use any above templates.
JdbcTemplate, NamedParameterJdbcTemplate are thread-safe i.e., they are single thread objects, so they allow single thread at a time.
A SimpleJdbcCall is a multi-threaded, reusable object representing a call to a stored procedure or a stored function.
It provides meta-data processing to
simplify the code needed to access basic stored procedures/functions.
All you
need to provide is the name of the procedure/function and a Map containing the
parameters when you execute the call.
The names
of the supplied parameters will be matched up with in and out parameters
declared when the stored procedure was created.
Java model class
Spring DAO class
DAO class implementation
Java based configuration file
Java Main Class
pom.xml file
Project Folder Structure
Create Procedure in database
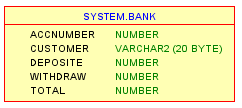
Create Table
Note: spring beans we can configure in 3 ways
1) xml based configuration file
Configure <beans> inside beans.xml file
2) annotation-based configuration
Configure <context:annotation-config/> inside beans.xml file and use annotations inside Java class.
3) Java based configuration
Configurations happen in Java file without xml file.
With the help of annotations like @configuration, @component, @service, @controller. etc.!










No comments:
Post a Comment